Aruba profile
A tourist magnet and a fuel exporter, Aruba is an autonomous territory of the Netherlands and one of the most prosperous territories in the Caribbean.
A tourist magnet and a fuel exporter, Aruba is an autonomous territory of the Netherlands and one of the most prosperous territories in the Caribbean.
Colonised by the Dutch in the 17th Century, Aruba lies 25km north of the coast of Venezuela. Away from the beaches, hotels and casinos, much of the island is desert-like but a strong indigenous heritage, colonisation and Latin American influence have given it a distinctive social and linguistic character.
A gold rush in the 1820s triggered an economic boom, with an oil refinery opening a century later. Its temporary closure in 1985 sparked an economic crisis and Aruba has since invested in tourism which is its economic mainstay.
Aruba is susceptible to drug smuggling and illegal immigration but has passed laws to combat money-laundering.
In 1986 Aruba pulled out of the Netherlands Antilles - a federation of Dutch Caribbean territories - and obtained separate status within the Kingdom of the Netherlands. The Dutch government controls defence and foreign affairs while the island's government handles local matters.
COUNTRY OF ARUBA: FACTS
Capital: Oranjestad
Area: 180 sq km
Population: 116,500
Languages: Papiamento, Dutch
Life expectancy: 73 years (men) 78 years (women)
LEADERS
Head of state: The King of the Netherlands, represented by a governor.
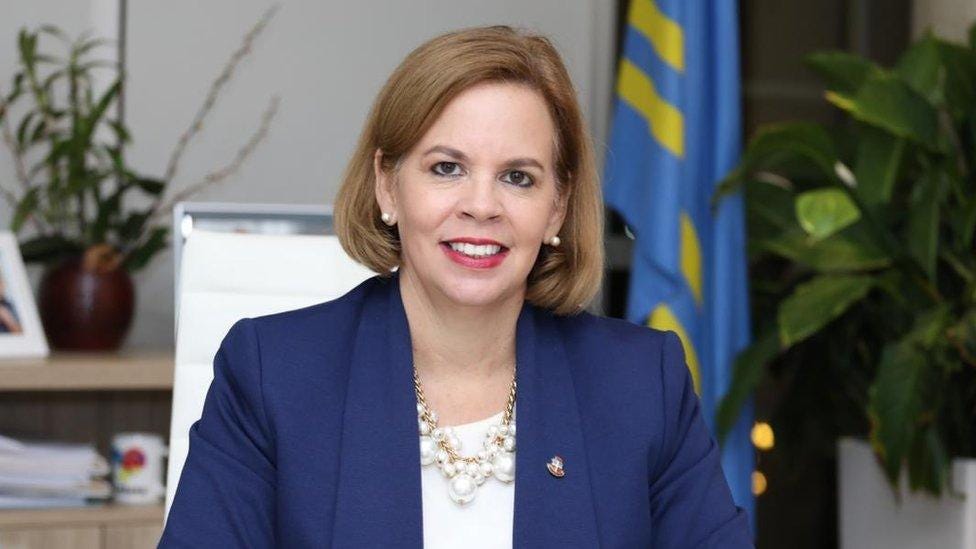
Prime minister: Evelyn Wever-Croes
Evelyn Wever-Croes was sworn in as Aruba's first female prime minister in November 2017.
A former tax lawyer, Wever-Croes began her political career in 2009 when she was elected to parliament as a member of the People's Electoral Movement (MEP). After only two years, she was elected to lead the party.
Under her leadership, the MEP won nine seats in the 2017 parliamentary elections, which allowed her to form a government with her coalition partners, Pueblo Orguyoso y Respeta (POR) and RED Democratico (RED).
She was returned to power after the June 2021 parliamentary elections at the head of a coalition government, as no party won an absolute majority.
MEDIA
Image caption,
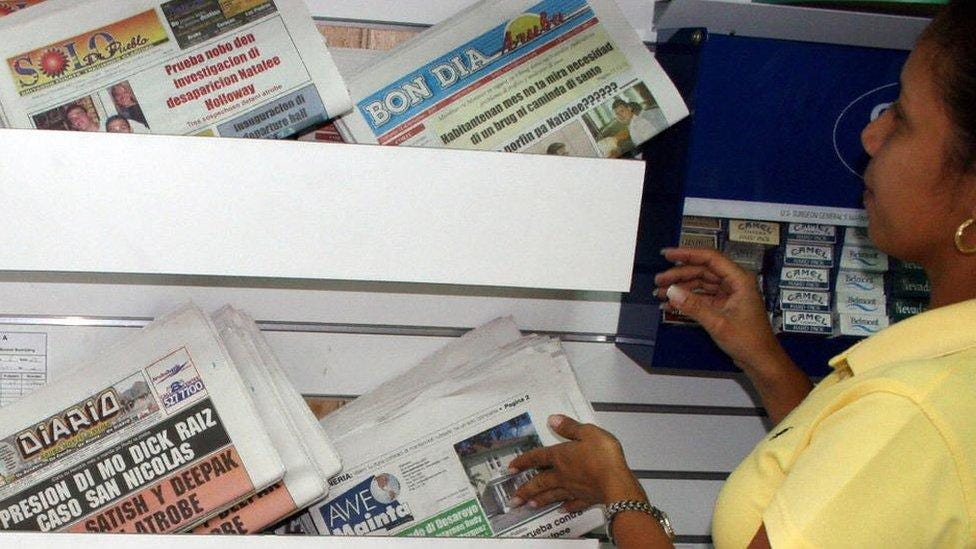
Papiamento-language newspapers are the most widely read dailies in Aruba
Aruba observes freedom of the press, as guaranteed under Dutch law. The mostly widely-read newspapers are in the Papiamento language.
There are two commercial TV stations. A cable TV subscription service provides access to foreign channels and there are a wide range of commercial radio stations available.
TIMELINE
Image caption,
Tourism has replaced oil refining as the island's economic mainstay
Some key dates in Aruba's history:
2500 BC-1515 - First inhabited by Amerindians of the Arawak tribe.
1499 - Spanish explorer Alonso de Ojeda discovers the island and claims it for Spain.
1636 - Aruba is colonised by the Dutch and forms part of the Dutch West India Company.
1806 - Aruba comes under British rule during the Napoleonic Was but is returned to the Dutch in 1816.
1954 - Aruba becomes part of the autonomous federation of the Netherlands Antilles.
1971 - Pro-independence struggle led by the People's Electoral Movement party (MEP) seek separation from Dutch Antilles administration.
1986 - Aruba obtains autonomous status within the Dutch kingdom.
1990 - Transition to full independence is postponed indefinitely at Aruba's request.
1996 - Aruba is included on US list of major drug-producing or transit countries.
2009 - OECD removes Aruba from an international list of uncooperative tax havens after it improves standards of transparency.
2017 - Evelyn Wever-Croes is sworn in as Aruba's first female prime minister.
Image caption,
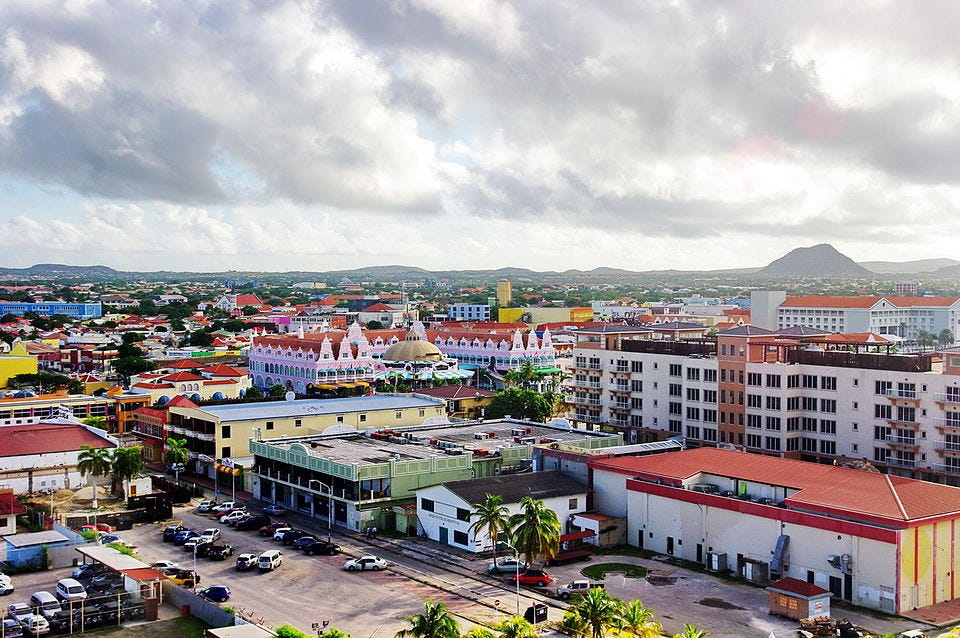
Aruba is the most touristed island in the southern Caribbean
The BBC
Economy of Aruba
The economy of Aruba is classified as a high income economy by the World Bank, with tourism currently providing the largest percentage of the country's income. Because of tourism's rapid growth on the island in the last 80 years, related industries like construction have also flourished in Aruba. Other primary industries include oil refining and storage, as well as offshore banking. Aloe cultivation, livestock, and fishing also contribute to Aruba's economy. In addition, the country also exports art and collectibles, machinery, electrical equipment, and transport equipment. Aruba's small labor force and low unemployment rate have led to many unfilled job vacancies, despite sharp rises in wage rates in recent years.
Economy of
Aruba
Centre of Oranjestad in 2011.
Currency
Aruban florin (AWG)
1 US$ = 1.80 AWG (Jan. 2025)
Fiscal year
Calendar year
Statistics
GDP
Increase $4.45 billion (nominal, 2025 est.)
Increase $5.9 billion (PPP, 2025 est.)
GDP growth
0.5% (2016) 2.3% (2017)
1.2% (2018e) 0.7% (2019e)
GDP per capita
Increase $41,498 (nominal, 2025 est.)
Increase $55,056 (PPP, 2025 est.)
Overview
Aruba's economy is a high-income economy heavily reliant on tourism, which generates the largest portion of its income. The island's economy is relatively concentrated on tourism, with a significant percentage of economic activity stemming directly or indirectly from this sector. While tourism drives growth, Aruba is also working to diversify its economy.
Here's a more detailed look:
Tourism: Aruba's tourism industry has shown resilience, bouncing back quickly from crises like the COVID-19 pandemic. It's a major employer and attracts foreign investment. The number of stay-over visitors has been increasing, and this growth is expected to continue, contributing to the overall economic expansion.
Economic Diversification: Aruba is actively working to diversify its economy beyond tourism. This includes attracting investments in other sectors and developing new industries.
Investment Climate: Aruba offers a favorable investment climate with strategic economic policies and infrastructure development.
Currency: The Aruban florin is the official currency, but the US dollar is widely accepted.
GDP: Aruba's nominal GDP for 2025 is projected to be 123.4% of the 2019 level.
Inflation: An inflation rate of 2.5% is expected for 2025.
MARUBA Model: The macroeconomic model MARUBA is used to facilitate economic projections for Aruba.