Bosnia-Herzegovina country profile
Bosnia-Herzegovina is an independent state which is partially under international oversight under the terms of the 1995 Dayton Peace Accords which ended the 1992-95 Bosnian war and the break-up of Yugoslavia.
More than 100,000 people were killed and around two million displaced in the war, which also left the infrastructure and economy in tatters.
Its three main communities are Bosniak Muslims, Croats and Serbs.
The country comprises two autonomous entities - the Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Republika Srpska - and the Brcko District, which is governed by its own local government. These come under a federal government and rotating presidency.
Peace has not brought the two entities closer together, and Bosnian Serb leaders often raise the possibility of seceding from what they call a failed state.
BOSNIA AND HERZEGOVINA: FACTS
Capital: Sarajevo
Area: 51,129 sq km
Population: 3.4 million
Languages: Bosnian, Croatian, Serbian
Life expectancy: 75 years (men) 79 years (women)
LEADERS
Chairman of the Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina: Denis Becirovic
Denis Becirovic has been the incumbent since March 2024.
The chair of the Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina is the presiding member of the Presidency of Bosnia and Herzegovina, which collectively serves as the country's head of state.
The chair rotates every eight months between a Serb, a Muslim, and a Croat. The responsibilities of the presidency lie largely in international affairs. In addition, the Muslim-Croat entity and the Bosnian Serb Republic each have their own presidents.
The three members elected at any one election serve a collective four-year term.
MEDIA
Ethnic divisions and the differences between the entities that make up Bosnia are evident in the media scene, and outlets run by the individual entities are more popular than the state-wide public broadcaster.
Divisions between the entities that make up Bosnia-Herzegovina are reflected in the media.
A lack of political consensus is reflected in the late rollout of digital TV and delays in passing laws on media ownership and public media funding.
TV is still the most popular medium but use of online media is increasing.
TV and radio outlets in Bosnia's two ethnic-based entities are more popular than the state public broadcaster, while commercial outlets struggle to make a profit in the crowded media market.
There are around 40 TV channels including three operated by public broadcasters, and 150 radio stations registered with the Communications Regulatory Agency.
TIMELINE
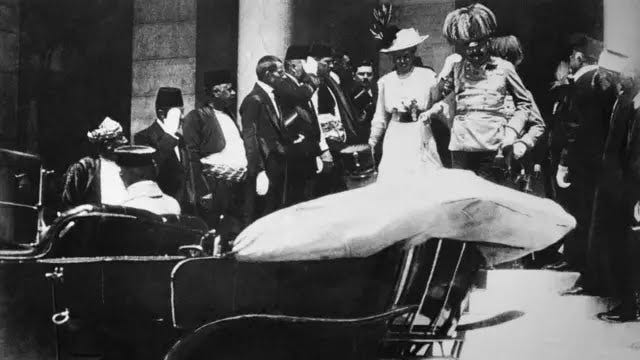
Image caption,The Austrian archduke Franz Ferdinand and his wife Sophia on their fateful visit to Sarajevo in June 1914
Some key dates in the history of Bosnia-Herzegovina:
1908 - Ottoman province of Bosnia-Herzegovina annexed by Austria-Hungary.
1914 - A Bosnian Serb student, Gavrilo Princip, assassinates the Austrian Archduke Franz Ferdinand in Sarajevo. This precipitates World War One.
1918 - Austria-Hungary collapses at the end of the war. Bosnia-Herzegovina becomes part of the future Yugoslavia.
1941 - Bosnia-Herzegovina annexed by pro-Hitler Croatian puppet state. Thousands of Serbs, Jews and Gypsies are sent to the death camps.
1945 - Bosnia-Herzegovina liberated following campaign by Communist partisans.
1945-1991- Bosnia is part of Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.
1992 - Following collapse of communism, Croat and Muslim nationalists form tactical alliance and outvote Serbs at independence referendum.
1992-1995 - Bitter ethnically-rooted civil war involving Bosnian Muslims, Serbs, and Croats. Serbs quickly assume control of over half the republic. Killings and deportations are rampant in the newly-proclaimed Serb Republic, but also widespread in Muslim and Croat-controlled areas.
Image caption,Civilians and Bosnian troops under Serbian sniper fire during the siege of Sarajevo in 1992
1995 - Safe haven of Srebrenica is overrun by Bosnian Serb forces under General Ratko Mladic, who massacre over 8,000 Muslims.
1995 December - Dayton Peace Accord creates two entities, one for Serbs and one for Bosnian Muslims and Croats. The Office of the High Representative is created to oversee its implementation. An international peacekeeping force is deployed.
2016 - Former Bosnian Serb leader Radovan Karadzic is convicted of genocide and war crimes for his role in the war.
Bosnia formally applies for EU membership.
2017 - Former Bosnian Serb military commander Ratko Mladic is found guilty of genocide and crimes against humanity during the Bosnian War. He is sentenced to life imprisonment.
2021 - Serb nationalist leader Milorad Dodik announces the RS will withdraw from Bosnia's military, its top judiciary body and tax administration, prompting renewed fears of a secession crisis.
2024 - Bosnia begins EU membership negotiations.
Image caption,Sarajevo is the political, financial, social and cultural centre of Bosnia and Herzegovina
Overview
Bosnia and Herzegovina is a country on the Balkan Peninsula in southeastern Europe. Its countryside is home to medieval villages, rivers and lakes, plus the craggy Dinaric Alps. National capital Sarajevo has a well preserved old quarter, Baščaršija, with landmarks like 16th-century Gazi Husrev-bey Mosque. Ottoman-era Latin Bridge is the site of the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand, which ignited World War I.
Fertility rate: 1.35 births per woman (2022) World Bank
GDP growth rate: 1.7% annual change (2023) World Bank
Gross domestic product: 27.05 billion USD (2023) World Bank
GDP per capita: 8,426.09 USD (2023) World Bank
Gross national income: 73.17 billion PPP dollars (2023) World Bank
Economy of Bosnia and Herzegovina
The economy of Bosnia and Herzegovina is a transitional, upper middle income economy. Bosnia and Herzegovina declared independence from socialist Yugoslavia on 1 March 1992. The main trading partners are Germany, Italy, Austria, Turkey and other neighboring Balkan countries.
Economy of
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Sarajevo, the financial centre of Bosnia and Herzegovina
Currency
Bosnia and Herzegovina convertible mark (BAM)
Fiscal year
Calendar year
Trade organisations
CEFTA, WTO (observer)
Country group
Developing/Emerging
Upper-middle income economy
Statistics
Population
Decrease 3,219,415 (1 January 2021, est.)
GDP
Increase $29.078 billion (nominal, 2024 est.)
Increase $74.28 billion (PPP, 2024 est.)
GDP rank
110th (nominal, 2023 est.)
110th (PPP, 2023 est.)
GDP growth
-3.0% (2020)
+7.4% (2021)
+4.2% (2022)
+1.8% (2023)
+2.5% (2024)
GDP per capita
Increase $8,221 (nominal, 2024 est.)
Increase $21,498 (PPP, 2024 est.)
Source: Wikipedia